A vision paper that dives into the potential for hyperloop in E-commerce
This notion explores a report on the challenges and opportunities facing the logistics industry in the rapidly changing world of e-commerce. With a focus on the year 2030, the paper examines the trends driving the growth of e-commerce, the consequences for logistics flows, and the potential of new technologies to transform the industry. In particular, the paper discusses the development of Cargoloop, and the role it could play in meeting the demands of e-commerce while reducing the industry's environmental impact. The paper concludes with a call to action for stakeholders across the industry to work together to realize the potential of these new technologies and create a more sustainable and efficient logistics ecosystem.
E-commerce challenges in 2030
E-commerce is driving significant changes in the retail landscape, and logistics must adapt to meet evolving customer needs. This section of the report explores the challenges facing e-commerce in 2030, with a particular focus on logistics. The chapter covers several key trends, including the growing demand for quick and on-demand delivery, the popularity of platforms and marketplaces, the trend towards multichannel retailing, and the impact of automation on fulfillment. These trends are driving significant changes in logistics, and businesses must adapt to remain competitive.
Key takeaways from this section include the following:
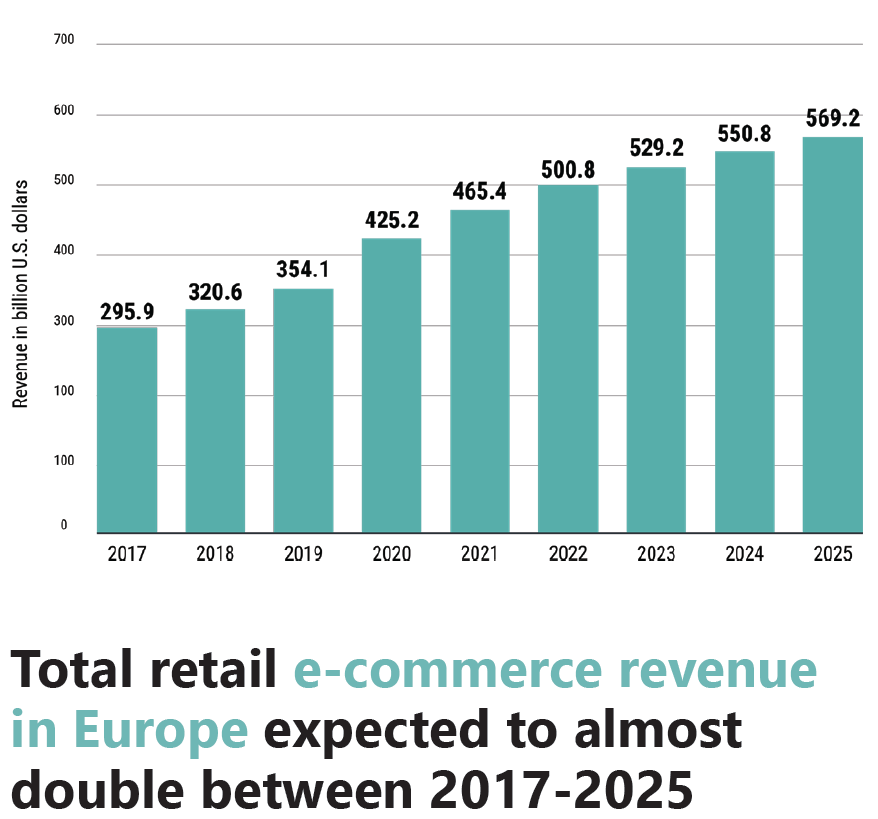
- Total retail e-commerce revenue in Europe is expected to almost double between 2017 and 2025 (see figure below).
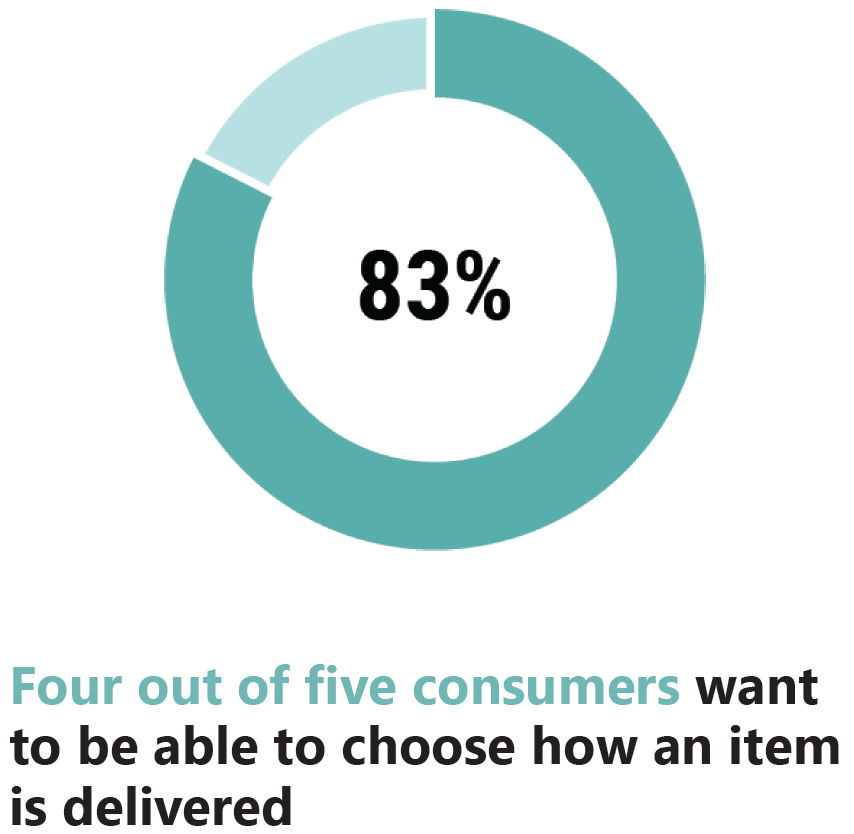
- Quick and on-demand delivery is becoming the norm in Western Europe, with customers expecting delivery within two days (see figure below).
- Platforms and marketplaces are increasingly popular, offering online sellers a route into the market.
- Multichannel retailing is on the rise, with businesses creating hybrid fulfillment networks to provide a seamless shopping experience across multiple channels.
- Automation is changing fulfillment, leading to centralization and the emergence of extra-large warehouses.
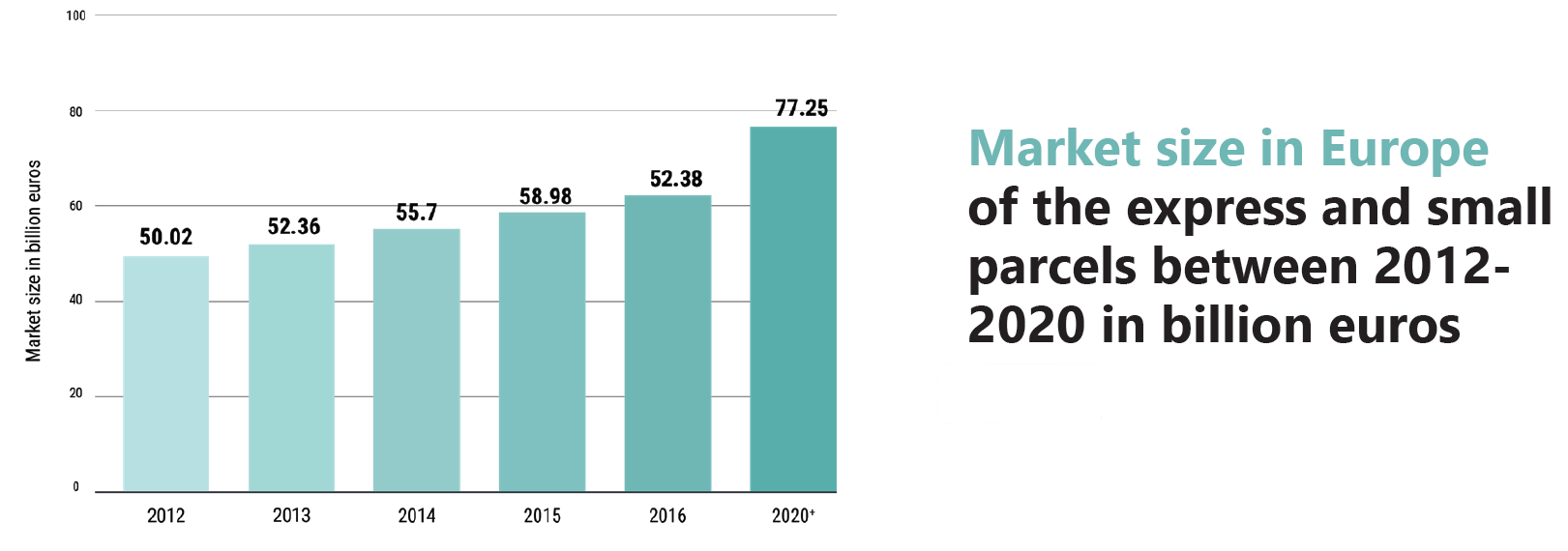
Consequences for logistics flows
This report section examines the consequences of e-commerce changes on logistics flows. It covers several topics, including the challenges of balancing stock locations and centralization, the importance of time and reliability in online retail, the growing demand for cross-border fulfillment, and the environmental impact of e-commerce. These trends are reshaping logistics, and businesses must adapt to meet the changing needs of customers while minimizing their environmental impact.
Key takeaways from this section include:
- The demand for cross-border fulfillment is on the rise, with the online cross-border market in Europe valued at approximately €146B in 2020.
- Balancing stock locations and centralization is challenging in meeting the demand for fast and on-demand delivery while reducing costs and complexity.
- Same or next-day delivery is increasingly critical for online retailers, with reliability being a key factor in customer satisfaction.
- E-commerce's environmental impact is a significant concern, with the need for more logistics real estate and increased traffic putting a strain on existing infrastructure.
Cargoloop: the future-proof modality for e-commerce
Cargoloop signifies a transformative evolution in the world of cargo transportation, brought to life by Hardt Hyperloop. Utilizing revolutionary hyperloop technology, Cargoloop transports parcels and pallets across a network of low-pressure tubes via magnetically levitated and propelled vehicles. This high-speed, autonomous operation enables continuous cargo transportation to their respective destinations without intermediate stops. Thanks to its efficient propulsion system and minimized drag, Cargoloop outshines other transport modes in terms of speed and energy efficiency. Designed to function on an open hyperloop network, it caters to all logistics companies and shippers alike.
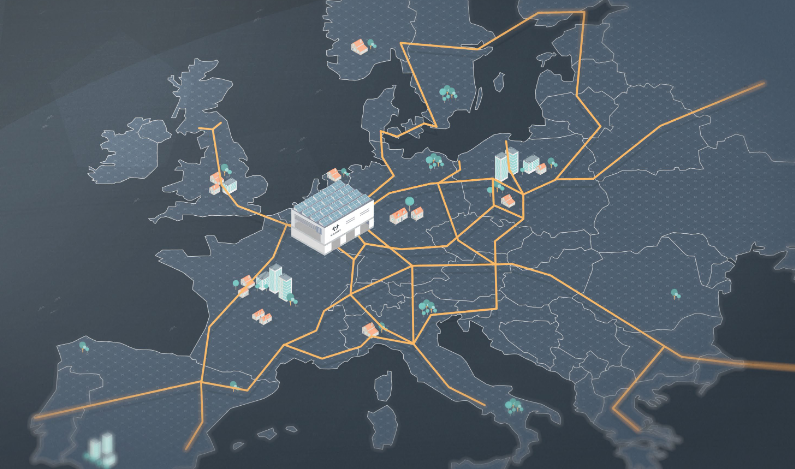
The envisioned European hyperloop network brings together European countries with high-speed core links capable of reaching 700 km/h (see figure below). Regional loops within these countries further establish connections with fulfillment locations such as logistics parks, cities, and other production and consumption centers. Specially tailored to integrate seamlessly into densely populated areas, these regional hyperloop connections offer a minimal visual impact and ensure a noise-free, vibration-less experience.
The Cargoloop vehicle, the central powerhouse in the hyperloop network, is optimized for the transport of parcels and pallets. Custom parcel containers, automatically loaded onto these vehicles, can accommodate between 150 and 300 parcels. The vehicles are designed to perfectly cater to pallet-sized freight, compatible with both Euro pallets and block pallets up to a height of 1.35 meters. By transporting smaller loads than traditional trucks, these vehicles optimize the load factor and frequency. Navigating autonomously, they also have the ability to align with other vehicles for energy and capacity optimization, while maintaining the ability to independently exit the network. Their capability to adapt to fluctuating demand patterns further adds to their utility.
The Cargoloop hub is a pivotal station where parcels are transferred from Cargoloop vehicles to other transport modes. Strategically located near logistics clusters and urban areas, these hubs are automated to ensure high throughput and reliable service, potentially operating round the clock. Equipped with loading docks for zero-emission, short-range freight vehicles, the hubs also potentially feature automated electric dollies or conveyors for nearby facilities. These hubs not only facilitate efficient parcel transfers but also promote the sustainability and on-demand delivery promise.
By offering same or next-day delivery from a central location without any emissions, Cargoloop helps businesses, especially online sellers, manufacturers, and brands to fulfill their promises while keeping costs and stock complexity manageable. Cargoloop further empowers small and medium-sized businesses across the EU by providing same or next-day delivery at affordable prices.
By targeting the middle mile of transportation, Cargoloop addresses the industry's challenge of reducing carbon emissions, potentially reducing them to zero and increasing speed by 300% to 800%. Lastly, Cargoloop plays a significant role in contributing towards a physical internet by providing a sustainable solution for time-sensitive shipments, ultimately bridging a major gap in the vision for a connected EU-wide co-modal transport service network.
How do we get there?
This section provides an overview of the challenges and opportunities involved in developing a sustainable, high-speed mode of transport for goods through the continental hyperloop network. The chapter discusses the need for showcasing and testing of core technologies, engagement with logistics industry and shippers, and support from public and policymakers. It also highlights the operational and control challenges and the importance of IT integration, data alignment, and stakeholder involvement.
The chapter stresses the urgency of taking action to accelerate the development of green modes of transport like hyperloop. It emphasizes the need to prioritize sustainable transportation solutions to address environmental concerns while meeting the growing demand for goods transport. Hyperloop technology has the potential to offer a sustainable and efficient mode of transport for goods, but further development and testing are required to overcome the technical and operational challenges.
Overall, this section emphasizes the need for collaboration between different stakeholders to develop and implement hyperloop technology successfully. It highlights the importance of investment in research and development and the need for policymakers to create an enabling environment for the adoption of sustainable modes of transport.

Acknowledgements



Hyperloop for E-commerce
This vision paper briefly explains the future e-commerce challenges and the consequences for logistics flows, and how hyperloop for cargo could potentially address these challenges as a future-proof modality for e-commerce. It concludes with answering the question of what the steps should be to realize a European hyperloop network for cargo.
The Amsterdam University of Applied Science and representatives of The Netherlands’ leading e-commerce companies have given valuable input on e-commerce fulfilment challenges and feedback on the Cargoloop concept and hub functionality through collaborative workshops to complete this vision paper.
The publication is accompanied by a video, produced by Hardt Hyperloop. Watch the video here https://youtu.be/llHNg5LFF-0
https://issuu.com/hardthyperloop/docs/visionpaper_ecommerce

